What is SD-WAN—Everything You Need to Know in One Spot
SD-WAN, or Software-Defined Wide Area Network, is a virtual network architecture that enables organizations to leverage a combination of different transport services to securely connect users to applications. These WAN transport services can include MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), LTE (Long-Term Evolution), and broadband internet. SDWAN transport options can be sourced from Tier-1 ISPs or local Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs)
The key aspect of SD-WAN is that it provides a software-defined approach to managing the wide area network, rather than a traditional hardware-centric model. This allows enterprises to choose the most appropriate transport services for their specific needs, whether that’s reliable MPLS for mission-critical traffic, cost-effective broadband for general internet access, or high-speed LTE for remote or mobile users.
The SD-WAN architecture abstracts the underlying transport technologies, giving the organization centralized control and visibility over the entire network. This provides benefits such as improved application performance, increased network reliability, simplified management, and the ability to leverage lower-cost internet connections alongside the MPLS backbone.
Overall, SD-WAN gives enterprises the flexibility and agility to adapt their wide area network to support evolving business requirements, while also optimizing costs and enhancing the user experience.
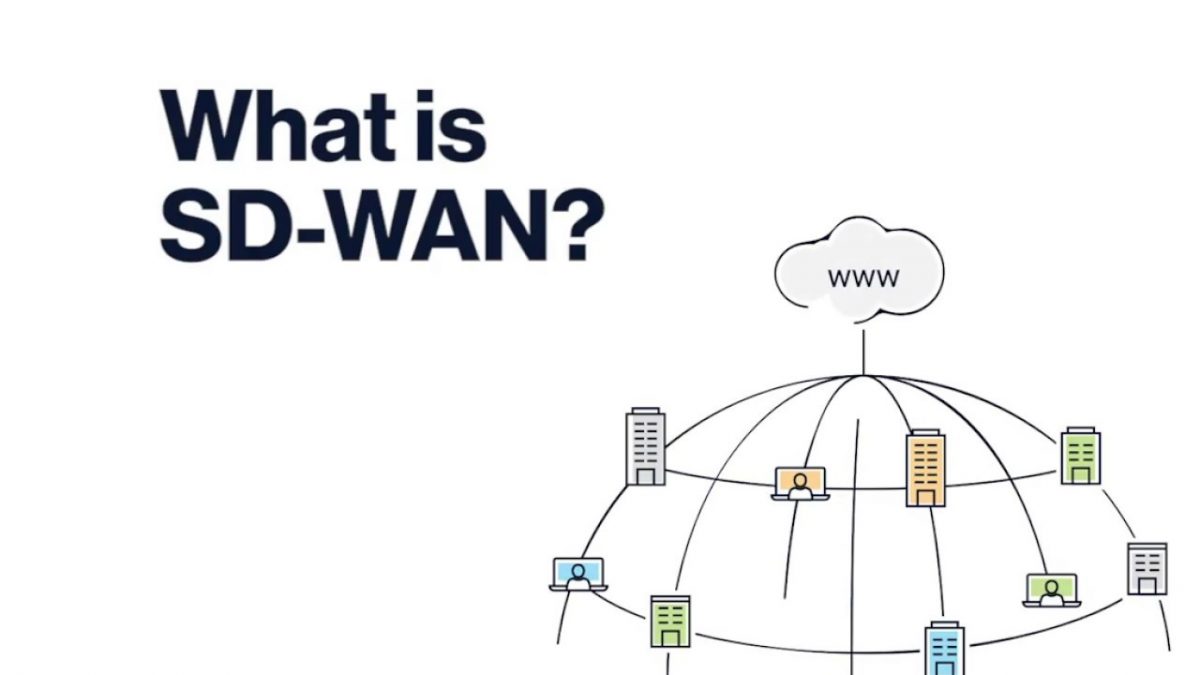
The business-wide area network (WAN) provides private connectivity between sites in a multi-location enterprise. As you can imagine, the technology has evolved substantially over the last few decades from basic point-to-point private line services to meshed network topologies. SD-WAN Explained will cover the latest in WAN transformation and describe the characteristics of Software Defined Wide Area Networks.
Evolution to SD-WAN
The evolutionary path up to today’s SD-WAN includes:
- Private Line (point to point)
- Frame Relay and ATM
- VPN and Network-Based VPN
- MPLS
- SD-WAN
The traditional WAN would enable users at a remote office to access applications hosted at a corporate data center. Simple point-to-point networks were often the go-to in this type of environment, but they could not scale to connect users for larger enterprises. Frame Relay and ATM packet-switched networking offered greater economies as a “host port” at a data center that could serve as the on-ramp for all the remote offices and the hub for most application flows. In this legacy design, generally, the data center would be the single gateway to the internet for all corporate users. Learn more about networking in our article entitled LAN vs WAN
As internet service providers expanded their presence and the number of global internet endpoints grew exponentially (Internet Growth Stats) business IT leaders and network service providers began to design and deploy WAN solutions using IPsec VPN tunnels across the internet. VPNs enable more dynamic private networks at a lower net cost than traditional private network solutions and can be highly secure due to inherent authentication and encryption capabilities.
MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching) is a packet-switched network technology that generally took over the market for frame relay and ATM networks and allowed many service providers to decommission their frame and ATM core switches. MPLS is now a common carrier core technology as it allows carriers to encapsulate and easily route other types of traffic, hence the name “multiprotocol”. The global market for MPLS is still strong and many large enterprises continue to buy and renew MPLS nodes, especially for sites in geographies where internet service routes are questionable or security is of high concern.
SD-WAN in the details:
SD-WAN or Software Defined Networking is the latest trend in enterprise networking. Macronet Services defines SD-WAN as an application-aware WAN technology that uses policy-driven decision-making to direct flows of network traffic over underlying network links. SD-WAN solutions include the SD-WAN edge (physical or virtual), network transport, and an Orchestration layer, which controls the policies and simplifies the management of the network by providing a source for detailed reporting.
SD-WAN benefits
The traditional WAN architecture was limited to enterprise, branch, and data center locations. However, as organizations have adopted cloud-based applications in the form of SaaS and IaaS, their WAN architecture has had to adapt to an explosion of traffic accessing applications distributed across the globe. These changes have brought multiple implications for IT, including potential compromises to employee productivity due to SaaS application performance problems, and rising WAN expenses from inefficient use of dedicated and backup circuits. IT teams have had to fight a daily, complex battle of connecting multiple types of users with multiple devices to multiple cloud environments.
SD-WAN offers several key benefits that help address these challenges:
Better application experience:
- High availability and predictable service for critical enterprise applications
- Utilization of multiple hybrid active-active links for all network scenarios
- Dynamically routed application traffic with application-aware routing for efficient delivery and improved user experience
- Reduced OpEx by replacing expensive MPLS services with more economical and flexible broadband, including secure VPN connections
More security:
- Application-aware policies with end-to-end segmentation and real-time access control
- Integrated threat protection enforced at the right places
- Secure traffic across broadband Internet and into the cloud
- Distribution of security to the branch and remote endpoints with NGFW, DNS security, and NGAV
Optimized cloud connectivity:
- Seamless extension of the WAN to multiple public clouds
- Real-time optimized performance for SaaS applications like Microsoft Office 365 and Salesforce
- Optimized workflows for cloud platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure
Simplified management:
- A single, centralized, cloud-delivered management dashboard for configuration and management of WAN, cloud, and security
- Template-based, zero-touch provisioning for all locations: branch, campus, and cloud
- Detailed reporting of application and WAN performance for business analytics and bandwidth forecasting
How does SD-WAN work for enterprises?
Unlike the traditional router-centric model, SD-WAN takes a software-defined approach to wide-area networking. The conventional router-centric model distributes the control function across all devices in the network, simply routing traffic based on TCP/IP addresses and access control lists (ACLs). This traditional model is rigid, complex, inefficient, and not well-suited for cloud environments, often resulting in a suboptimal user experience.
In contrast, an SD-WAN architecture enables cloud-first enterprises to deliver a superior application quality of experience (QoE) for users. By identifying and classifying applications, an SD-WAN can provide intelligent, application-aware routing across the wide area network. This allows each class of applications to receive the appropriate quality of service (QoS) and security policy enforcement, all tailored to the organization’s business needs.
Additionally, SD-WAN enables secure local internet breakout of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) and software-as-a-service (SaaS) application traffic directly from branch locations. This provides the highest levels of cloud performance while also protecting the enterprise from potential threats, as the traffic does not have to traverse the entire network to reach the cloud.
The SD-WAN Marketplace
The market for SD-WAN is growing rapidly and is expected to surpass $6B in 2023 as enterprises adopt SD-WAN as their primary technology for connecting their locations and cloud services. The decision to move to SD-WAN is typically driven by the IT leader’s focus on the “end-user experience” and the need to enable secure high-performance connectivity directly to cloud-based business applications. Further, SD-WAN can layer on a full stack of security features and functions to combine into what is now called a Secure Access Service Edge, or SASE. SASE architectures may now incorporate next-generation security features such as:
- IDS/IPS
- Secure Web Gateways
- Anti-Malware
- DDOS Mitigation
- CASB
You can learn more about the SASE model (Here).
A Summary of SD-WAN Characteristics Includes:
Network Agnostic: SD-WAN is network agnostic, meaning it can leverage multiple types of network links at a single site. This could include MPLS, broadband internet, LTE, or any other available transport options. This flexibility allows organizations to utilize the most cost-effective and appropriate connectivity for each location.
Meshing: With SD-WAN, all sites can be fully meshed if desired. This means each location has direct connectivity to every other location, rather than a hub-and-spoke model. This improves application performance, redundancy, and overall network resilience.
Security: SD-WAN can include a full stack of security functions, such as firewalling, encryption, and threat protection. These security capabilities can be centrally managed and enforced, even at the branch level, providing consistent policy enforcement across the entire network.
Application Control: SD-WAN makes packet forwarding decisions based on application-aware policies. This means the network can intelligently route traffic to optimize performance for critical applications, while also applying the appropriate security and quality of service (QoS) controls.
Automation: The centralized management capabilities of SD-WAN enable simplified automation of network configurations and changes. This includes features like zero-touch provisioning, which allows new sites to be added to the network with minimal manual intervention.
Visibility: SD-WAN provides centralized visibility into routing, application performance, and other network metrics. This gives IT teams better insights into how the network is performing and where optimizations may be needed.
Reporting: In addition to visibility, SD-WAN systems offer detailed reporting across the wide area network. This includes historical trends, bandwidth utilization, and other analytics that can inform business decisions and network planning.
Availability: SD-WAN’s use of multiple network links and high availability (HA) designs helps enhance overall network uptime and resiliency. If one link fails, traffic can be dynamically rerouted across the remaining active connections.
Efficiency: SD-WAN allows organizations to fully utilize their available bandwidth by intelligently directing applications to the most appropriate link types based on factors like performance requirements, cost, and security needs.
Procuring the right SD-WAN solution for your enterprise might seem like an overwhelming task due to the ever-expanding list of available solutions. Macronet represents hundreds of suppliers and the team at Macronet Services can help you define the ideal architecture and efficiently navigate the options. In the discovery process, we will use our tools and experience to help you consider:
- Locations
- Connectivity
- Data Applications
- Real-Time Applications
- Security
- Disaster Recovery
- Wireless Access Points
- Reporting & Analytics
- Current Inventory and Other WAN Environments
- Business Considerations
SD-WAN Offerings
At Macronet Services, we see various sourcing trends that are driven by factors that are very specific to each of our clients. SD-WAN procurement models generally include:
- Customer Managed
- Carrier Integrated
- Managed Service Provider Overlay
- Network-Based
Some clients are highly sophisticated and have the ability to deploy and support SD-WAN edge and Orchestration solutions on their own, but most businesses do not have the desire to invest in the depth of resources for a customer-managed model.
Carrier Integrated solutions are very common globally since many network service providers have built the SD-WAN orchestration layer and network-based security into their network and most carriers already have experienced managed services operations teams. In this model, you can source both network circuits and the SD-WAN edge from your network service provider. Carriers generally align with several SD-WAN technology partners such as VMWare Velocloud, Versa Networks, Cisco Viptela, Silverpeak, or other leaders.
Managed Service Provider Overlay networks can be sourced from a growing number of MSPs who focus specifically on designing, deploying, and implementing SD-WAN solutions for businesses. These solutions can be deployed over the top of existing WANs and typically provide 24x7x365 monitoring and support. Some MSPs have developed sophisticated internal tools to manage deployments and to integrate with enterprise ticketing systems. Each has its own strengths and the Macronet Services team can quickly help identify a short list of viable options for your business.
Network-Based SD-WAN solutions are continuing to gain market share and are a great fit for certain enterprise users. In this model, the SD-WAN service provider has built out a global network of PoPs using various Tier 1 carriers and can offer SLAs across their core network. Enterprises connect to the network using IPsec VPN or may deploy an appliance at the customer’s edge. The SD-WAN core typically includes a list of enhanced security features and options such as remote access.
Looking Ahead in SD-WAN
As noted in this article, the SD-WAN market will continue to grow rapidly and the total number of options will continue to expand as service providers and technology vendors integrate more capabilities into their products. The movement towards the co-managed SASE SD-WAN model will increase in velocity as attack surfaces increase due to cloud and remote networking initiatives.
Regarding the WAN component, the SD-WAN architecture will include more 5G and LEO satellite links as performance metrics improve for these services and enterprises demand rapid deployment of secure high-bandwidth solutions. IOT adoptions will drive the need for highly granular segmentation based on the device class and the required security posture of each class.
Managed SD-WAN service providers will work to maintain an edge by developing and enhancing their own Intelligent Process Automation and AIOps (AI for IT Operations) solutions. Some will build their own SIEM/SOC product offerings to service clients who need to outsource security operations.
Enterprise users will benefit greatly by selecting MSPs who can align best with their needs and serve as a seamless and cost-effective extension of their IT operations. Contact Us at Macronet Services to have a conversation about how we can help your team design, source, and govern your WAN in partnership with your IT team.
Related Posts
15 Comments
Comments are closed.
Recent Posts
- The Complete Oracle FastConnect Guide: Architecture, Routing, Security, and Enterprise Connectivity Design
- Telecom Expense Management (TEM): The Definitive Guide for Mid-Large Enterprises
- Designing Secure and Compliant Networks in China: The Definitive Guide for Global Enterprises
- Securing Autonomous AI Agents: Identity-Anchored Autonomy for Enterprise Risk & Resilience
- The Definitive Guide to Enterprise Telecom Agreements: MSA, SLA, and DIA Negotiation Best Practices for Global Carriers
Archives
- December 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- December 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
Categories
- Clients (12)
- Telecom Expense Management (1)
- Satellite (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (9)
- Travel (1)
- Sports (1)
- Music (1)
- News (282)
- Design (4)
- Uncategorized (1)
- All (19)
- Tips & tricks (25)
- Inspiration (9)
- Client story (1)
- Unified Communications (196)
- Wide Area Network (309)
- Cloud SaaS (60)
- Security Services (71)





[…] you need SDWANpost Covid as all of your corporate apps reside in AWS & you have adopted UCaaS? Perhaps […]
[…] software-defined network (SDN). MVE provides the edge-networking architecture that supports partner SD-WAN technology directly on Megaport’s […]
[…] team at Macronet Services helps IT teams design and source the best options for SD-WAN and cloud-based collaboration tools including Unified Communications as a Service and Contact […]
[…] in the swiftness of change, teams did not realize what they were losing from a traditional carrier SDWAN. Often, they did not have to architect a truly low-latent, cost-effective cloud networking path […]
[…] location such as your other cloud instance, datacenter, WAN etc. As we look at the landscape of SDWAN, may companies have opted to push more workloads to public cloud, especially Oracle an remove less […]
[…] Wide Area Networks (WANs):A rising tide in the SDWAN environment is organizations ditching this architecture in favor of a Zero Trust network. As […]
[…] if not, open a trouble ticket with your carrier before the sun rises. As more companies opt for SDWANreplacing legacy MPLS networks, they invariably add 1-5+ carriers in their network across Broadband, […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]
[…] SDWAN […]